 We are interested in combining microwave heating with continuous flow methods for the synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles. Our goal is to improve the quality of synthesized nanoparticles and minimize run-to-run variation. Colloidal nanoparticles are synthesized using several consecutive stages, including activation of precursors, formation of nuclei, growth of nanoparticles from the nuclei, and isolation of nanoparticles of the desired size.
We are interested in combining microwave heating with continuous flow methods for the synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles. Our goal is to improve the quality of synthesized nanoparticles and minimize run-to-run variation. Colloidal nanoparticles are synthesized using several consecutive stages, including activation of precursors, formation of nuclei, growth of nanoparticles from the nuclei, and isolation of nanoparticles of the desired size.
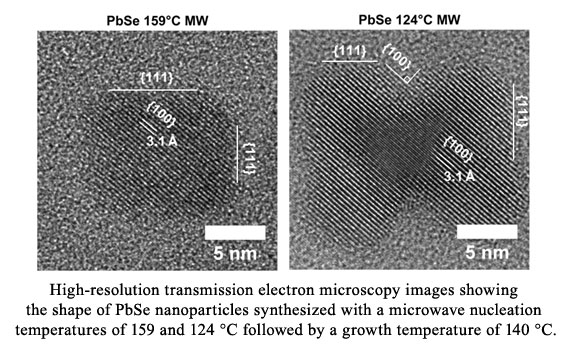
The separation of the nucleation event from the growth stage is necessary to obtain a homogeneous size distribution. For our studies the microwave zone is used for rapid volumetric heating that enhances the kinetics of nuclei formation, while an oil bath is used for the growth zone. Using continuous flow methods we are able to separate the kinetic and thermodynamic processes
The microwave assisted continuous flow reactor is applicable to many types of nanoparticles including semiconductor nanoparticles for solar cells, quantum dots for lighting and display applications, as well as metal organic framework materials. Funding for this research is provided through ONAMI, Oregon BEST, Oregon State University Venture Fund, and ARPA-e.