Methodology:
The 5-Step Work Improvement Process, seen graphically below, starts by tracking the organization’s system health (Step 1). Next, the organization’s employees take a three-part survey, named the Good Work Questionnaire followed by in-person interviews between workers and the researcher (Step 2). Based on the results of Step 2, potential mismatches will be identified by the GWT Team (Step 3). Once mismatches are identified, the GWT Team will work with the organization to find improvement actions (Step 4) that the organization can choose to implement (Step 5). The Good Work Process can be repeated for continuous improvement. Click here to learn more about the Good Work Questionnaire.
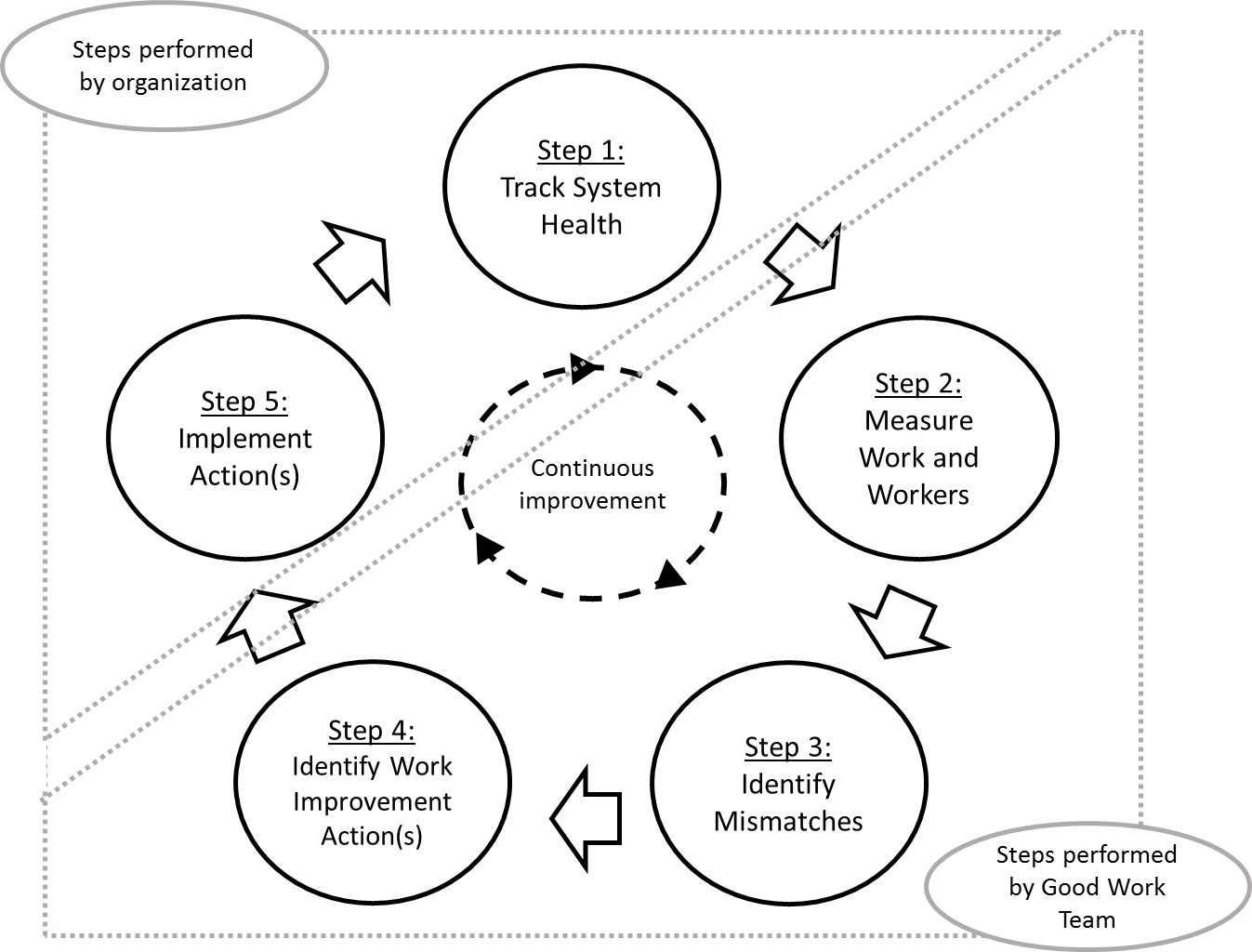
Each step of the 5-Step Work Improvement Process is explained further below.
Step 1) Track System Health
Tracking system health is performed by recording common indicators such as turnover and absenteeism. The system health may also be tracked using productivity indicators such as, quantities produced, defect rates, and costs. Establishing these metrics initially, provides a benchmark for system health. Tracking these metrics over time allows comparison to the prior period. Tracking survey responses over the same time period allows a user to see if the implemented measures have been effective.
Step 2) Measure Work and Workers
Using an electronic questionnaire titled the Good Work Questionnaire, workers rate their satisfaction with their current work based on twelve dimensions of work. Additionally, workers rate their personal importance of each dimension when assessing their work.
Step 3) Identify Mismatches
Mismatches are identified between the ratings of current work and the personal importance of the population of workers surveyed. Dimensional differences are calculated for each work dimension by: subtracting the population’s importance rating of the dimension from the rating of the current work offered by the company. Statistically significant differences are considered a mismatch between the workers’ needs and the work offered. A p-value of less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant, which means that there is less than five percent probability (1 in 20) that the difference between ratings of current work and desired work is only due to variation between respondents.
Step 4) Identify Work Improvement Actions
Dimensional mismatches are addressed using Work Improvement Actions, also referred to as work improvement measures, developed in Dr. Lee’s research. For each work dimension in need of redesign, several work redesign measures are recommended in order to mitigate the mismatch. These improvement action are continually being updated and are based on past work redesign efforts from automotive and marine manufacturers in Europe, Japan, Brazil, and the United States.
Step 5) Implement Actions.
Implement, or put into action, the recommended improvement actions. This step in the work improvement process can be performed only by the organizations management/ leadership.